Advertisement
When we think of cyber attacks, what often comes to mind are the flashy headlines—massive data leaks, high-profile hacks, or ransomware shutting down companies. But there's a silent troublemaker operating just under the radar, often left unchecked: SQL injection. It doesn’t require an entire hacking squad or some elaborate phishing campaign. Instead, it exploits something most websites already rely on—databases. And that makes it sneakier than most people realize.
You’d be surprised how many popular websites remain vulnerable to this attack. Even companies that seem to be buttoned-up on cybersecurity can fall into this trap. Why? Because SQL injection hides in plain sight. It’s not flashy, but it’s devastating. One overlooked line of code is sometimes all it takes.

To put it simply, SQL injection (often shortened to SQLi) is a way attackers manipulate database queries by exploiting unvalidated user input. Most websites and applications use SQL (Structured Query Language) to fetch or modify information, like login credentials, product lists, or user profiles. And that's exactly where the risk begins.
Imagine a basic login form with fields for username and password. When you enter your details, the backend might generate a query like this:
sql
CopyEdit
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = 'user' AND password = 'pass';
Now, if the application doesn’t properly check what’s typed into those fields, someone could slip in a string like:
bash
CopyEdit
' OR '1'='1
The query then turns into:
sql
CopyEdit
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '' OR '1'='1' AND password = '';
And since '1'='1' always returns true, the database just lets the attacker right in—no password needed.
This kind of vulnerability doesn’t rely on breaking encryption or installing malicious software. It just takes advantage of sloppy coding. The attacker doesn’t need to upload files or trick users—they just need one poorly protected input box. That’s all.
Once inside, they can do far more than just look around. SQL injection can leak private data, alter records, delete content, or even allow full control over the system, depending on how much access the database user has. In some cases, it doesn't stop at the data layer. It opens the door to the entire server.
So no, your firewall won’t always catch it. And your antivirus won’t see it coming. The real problem isn’t a lack of defense tools—it’s trusting user input without question. That’s the crack where SQL injection slips through.
Let’s break it down.
This is the classic goal. Attackers might want usernames, email addresses, or financial information. SQL injection is incredibly efficient for this.
Sometimes it's not about stealing data, but changing it. Consider someone tampering with product prices, modifying order records, or altering admin credentials. A single rogue command can alter thousands of records instantly.
In some cases, attackers don’t just tweak data—they take over. That includes creating new users with administrative privileges, installing backdoors, or making the database run harmful scripts.
Advanced SQL injection attacks can pivot from database access to full server control, especially if the database has elevated permissions. From there, the entire infrastructure is at risk.
Now here’s the scary part: many SQL injection attacks go unnoticed for days, even weeks. There’s no obvious alarm. No flashing red lights. Just quiet exploitation behind the scenes.
SQL injection isn’t one-size-fits-all. There are a few variations, and knowing how they differ helps understand how wide the threat really is.
This is the most straightforward method—manipulating inputs through a form, search bar, or login page. If the site echoes back database errors, attackers can experiment and refine their queries.
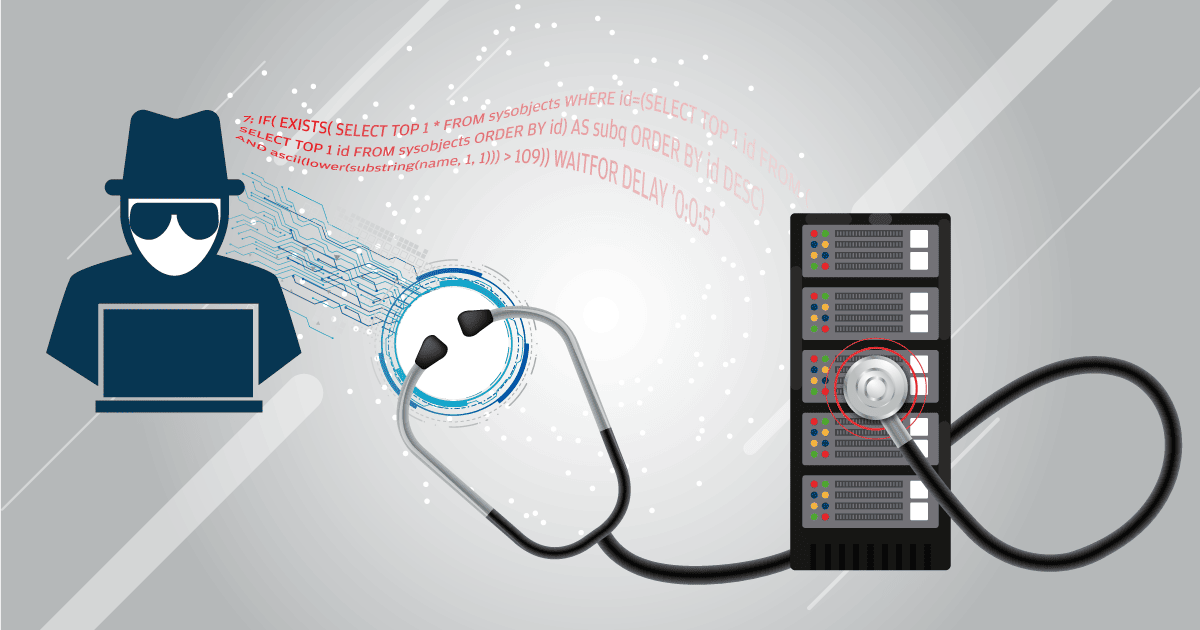
If the app doesn't show errors or outputs directly, hackers get creative. They send queries that change behavior based on the database's response, timing, boolean logic, or content differences. It's called "blind" because there's no direct feedback, but it's just as dangerous.
This one's rare but powerful. It sends data to another server under the attacker’s control, often through HTTP requests or DNS lookups. It’s used when regular channels don’t work or are too slow.
Here, the harmful SQL doesn't run right away. Instead, it's stored somewhere in the database and only gets executed later, perhaps when an admin views a report. It's more subtle and harder to trace.
This is the gold standard. Instead of building queries with user input mashed into a string, parameterized queries keep the SQL separate from the data. The database knows where the command ends and the input begins.
In PHP with PDO, for example:
$stmt = $pdo->prepare('SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?');
$stmt->execute([$username]);
This small change blocks most injection attempts completely.
Never trust user input—even if it looks safe. Validate data types (is it an email? a number?) and reject anything unexpected. Escaping special characters is a secondary layer, especially useful in older systems.
Your web application doesn’t need to control the entire database. Set user roles smartly. If the app only reads data, it shouldn’t have permission to delete or update. If the worst happens, you want the damage to be limited.
Verbose error messages are helpful during development, but in production, they act like roadmaps for attackers. Instead of revealing SQL syntax or table names, return a generic error. Log the real message somewhere secure.
While they’re not foolproof, WAFs can help filter out known attack patterns before they hit your server. They buy you time and catch sloppy attempts.
SQL injection isn’t flashy, but it’s effective—and that’s exactly what makes it so dangerous. It takes advantage of a simple oversight and turns it into a full-blown breach. No extra hardware, no social engineering—just one line of malicious code in the right place.
The good news? It’s also one of the easiest vulnerabilities to fix—if you pay attention.
Use parameterized queries. Validate input. Set smart permissions. Don’t assume your system is safe just because nothing’s gone wrong yet.
Because the real threat isn't when an attacker crashes through the front door, it's when they quietly walk in through the side, take what they need, and leave without a trace.
Advertisement

Explore Proximal Policy Optimization, a widely-used reinforcement learning algorithm known for its stable performance and simplicity in complex environments like robotics and gaming
How Summer at Hugging Face brings new contributors, open-source collaboration, and creative model development to life while energizing the AI community worldwide

Confused about DAO and DTO in Python? Learn how these simple patterns can clean up your code, reduce duplication, and improve long-term maintainability

Heard of Julia but unsure what it offers? Learn why this fast, readable language is gaining ground in data science—with real tools, clean syntax, and powerful performance for big tasks

Discover how Google BigQuery revolutionizes data analytics with its serverless architecture, fast performance, and versatile features

Struggling with a small dataset? Learn practical strategies like data augmentation, transfer learning, and model selection to build effective machine learning models even with limited data

How accelerated inference using Optimum and Transformers pipelines can significantly improve model speed and efficiency across AI tasks. Learn how to streamline deployment with real-world gains
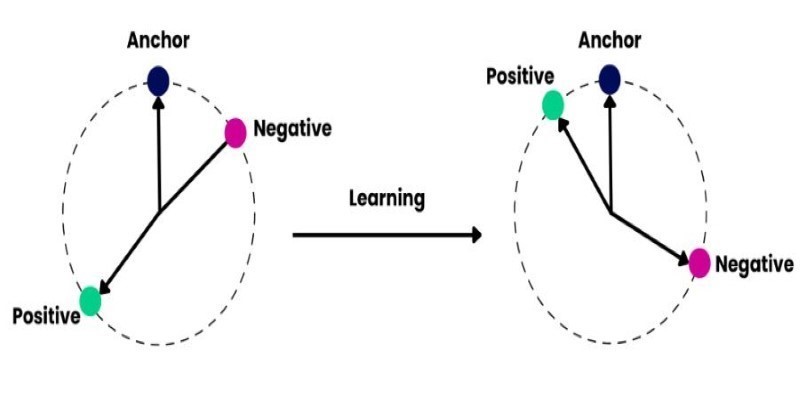
How to train and fine-tune sentence transformers to create high-performing NLP models tailored to your data. Understand the tools, methods, and strategies to make the most of sentence embedding models

What does GM’s latest partnership with Nvidia mean for robotics and automation? Discover how Nvidia AI is helping GM push into self-driving cars and smart factories after GTC 2025

Improve automatic speech recognition accuracy by boosting Wav2Vec2 with an n-gram language model using Transformers and pyctcdecode. Learn how shallow fusion enhances transcription quality
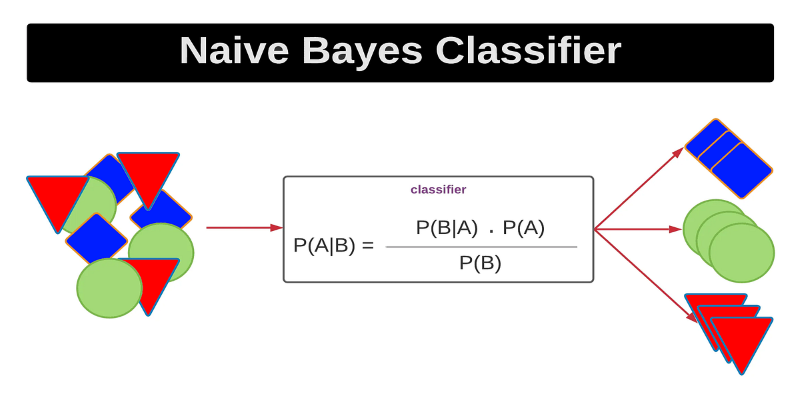
Curious how a simple algorithm can deliver strong ML results with minimal tuning? This beginner’s guide breaks down Naive Bayes—its logic, types, code examples, and where it really shines

The Hugging Face Fellowship Program offers early-career developers paid opportunities, mentorship, and real project work to help them grow within the inclusive AI community